
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Secure Docker Compose Script with VPN Integration
- Preston Bernstein
- Docker tutorials , VPN and security , Dev ops , Containerization , Networking , Cloud computing , Cybersecurity , Software development , It infrastructure , Tech how tos
- June 20, 2024
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, safeguarding online activities is crucial. Docker is widely used for deploying and managing applications, making their security essential. VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) offer a robust solution by protecting services from unauthorized access and keeping data private.
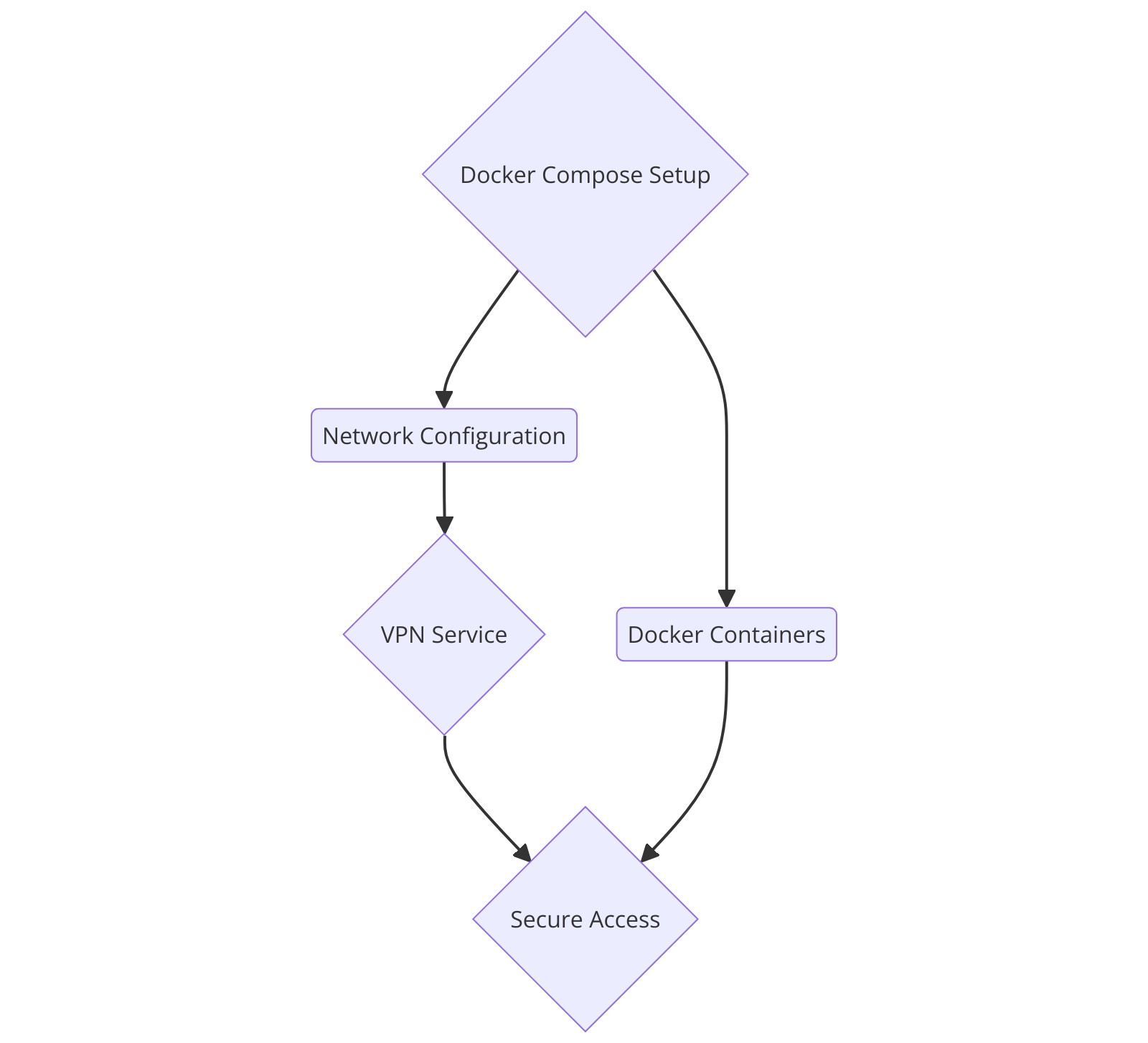
This guide will show you how to create a Docker Compose script that places each service securely behind a VPN. Whether you’re working on a small project or a large-scale application, integrating a VPN with Docker Compose can significantly enhance your security. We’ll cover the basics of Docker Compose and VPNs, followed by step-by-step instructions for setup and configuration. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a secure setup with your Docker services protected by a VPN, safeguarding your data and applications from potential threats.
While it’s not required, having a basic understanding of Docker is recommended before reading this article. If you need to learn more about Docker, the official Docker documentation is a great resource.
Overview of Docker Compose and VPNs
What is Docker Compose?
Docker Compose simplifies the deployment of multi-container Docker applications by allowing developers to define services, networks, and volumes in a single YAML file. This approach streamlines the management of containerized applications, enabling easy configuration and launching of complex applications with just a few commands.
Benefits of Docker Compose
- Simplifies multi-container deployments
- Ensures consistency across development, testing, and production environments
- Streamlines application scaling and maintenance
Typical Use Cases
- Microservices architecture
- Development environments
- Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines
Why Use a VPN with Docker Services?
Integrating a VPN with your Docker services enhances both security and privacy. A VPN encrypts network traffic, preventing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive data. This is especially important when Docker services interact with external networks or handle confidential information.
Common Scenarios and Benefits:
- Securing communications between distributed services
- Protecting data in transit from eavesdropping
- Ensuring privacy for services that need to access external resources

Understanding the Challenge
Configuring networking and container isolation in Docker can be challenging. By default, Docker containers share the host’s network stack, which can lead to potential security risks. Isolating each service behind a VPN helps mitigate those risks.
Issues with Networking and Container Isolation
- Potential exposure of sensitive data
- Difficulty in managing network policies
- Ensuring consistent VPN connections for all services
By understanding these challenges and implementing a VPN within your Docker Compose setup, you can create a more secure and reliable environment for your applications.
Setting Up Docker Compose
Installing Docker and Docker Compose
Steps to Install Docker:
Update Your Package Database:
Ensure your system’s package database is up-to-date
sudo apt update
Install Prerequisite Packages
Install packages that allow apt to use repositories over HTTPS
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
Add Docker’s Official GPG Key:
Add Docker’s GPG key to verify the integrity of the software.
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Add Docker Repository:
Add Docker’s official repository to your sources list.
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
Install Docker:
Update the package database again and install Docker.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker-ce
Verify Docker Installation:
Confirm Docker is installed correctly by running:
sudo docker --version
Steps to Install Docker Compose
Download the Latest Version:
Download the Docker Compose from its official Github repository.
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Apply Executable Permissions:
Make the downloaded file executable.
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Verify Docker Compose Installation:
Check the version to ensure Docker Compose is installed.
docker-compose --version
Creating a Docker Compose File
Basic Structure of a docker-compose.yml File:
A docker-compose.yml file defines the services, network, and volumes used in your application. Here is the basic structure:
version: '3.8'
services:
# Define your services here
networks:
# Define custom networks if needed
volumes:
# Define named volumes if needed
Explanation of Key Directives:
version: Specifies the version of the Docker Compose file format.
services: Defines the containers to be run as the part of the application.
- image: Specifies the Docker image to use.
- build: Allows specifying a build context and Dockerfile.
- ports: Maps container ports to host ports.
- volumes: Mounts host paths or named volumes.
- networks: Connects services to specific networks.
networks: Customized networking configurations for services.
volumes: Manages data persistence using named volumes.
Example: Basic Docker Compose File
Here’s a simple example with two services: a web server and a database.
version: '3.8'
services:
web:
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- "80:80"
networks:
- webnet
database:
image: postgres:latest
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: exampleuser
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: examplepass
POSTGRES_DB: exampledb
volumes:
- db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- webnet
networks:
webnet:
volumes:
db-data:
By understanding the basic structure and following these steps, you can create a Docker Compose file that efficiently sets up and manages your services.
Configuring Each Service to Use the VPN
Choosing a VPN Provider
When selecting a VPN provider for your Docker setup, it’s essential to consider several key factors to ensure optimal performance and security:

Key Factors to Consider:
- Reliablity: Choose a provider with a reputation for uptime and reliability.
- Security Features: Ensure the provider offers strong encryption and no-log policies.
- Compatibility: Verify that the VPN service is compatible with Docker and can be used within containers.
- Performance: Consider the speed and latency, especially if your servicers require high bandwidth.
- Support: Look for providers that offer good customer support and detailed documentation.
Example: Using OpenVPN or Another Common VPN Service:
OpenVPN is a popular choice due to its flexibility, strong security, and open-source nature. Another option is WireGuard , known for its simplicity and performance. Both can be used effectively with Docker.

Setting Up the VPN Container
Pulling a VPN Container Image (e.g., OpenVPN):
To set up a VPN container, you will first need to pull the appropriate image from Docker Hub. Here’s how you can do it using OpenVPN:
docker pull kylemanna/openvpn
This command downloads the OpenVPN image, which you can then use to create and configure your VPN container.
Configuring the VPN Container:
- Initialize the OpenVPN Configuration: Create a directory to store the OpenVPN configuration and initialize it:
mkdir -p /path/to/your/config
docker run -v /path/to/your/config:/etc/openvpn kylemanna/openvpn ovpn_genconfig -u udp://YOUR_VPN_SERVER
This command sets up the necessary configuration for OpenVPN in the specified directory.
- Generate the Certificates: Generate the necessary certificates and keys:
docker run -v /path/to/your/config:/etc/openvpn -it kylemanna/openvpn ovpn_initpki
This command initializes the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), generating the certificates and keys required for OpenVPN.
- Start the OpenVPN Container: Start the container with the generated configuration:
docker run -v /path/to/your/config:/etc/openvpn -d -p 1194:1194/udp --cap-add=NET_ADMIN kylemanna/openvpn
This command runs the OpenVPN container in detached mode, mapping the required port and granting the necessary network administration capabilities.
Modifying the Docker Compose File
Adding the VPN Container to the docker-compose.yml File:
To integrate the VPN container into your Docker Compose setup, modify your docker-compose.yml file to include the VPN container and configure your services to use it.
Configuring Services to Route Traffic Through the VPN:
Ensure your services are configured to route their traffic through the VPN container by setting the network mode of the service to the VPN container.
Example: Updated Docker Compose File with VPN:
Here’s a step-by-step example:
version: '3.8'
services:
vpn:
image: kylemanna/openvpn
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN
ports:
- "1194:1194/udp"
volumes:
- /path/to/your/config:/etc/openvpn
environment:
- OPENVPN_PROVIDER=YourProvider
- OPENVPN_CONFIG=YourConfig
networks:
- vpn_net
web:
image: nginx:latest
depends_on:
- vpn
network_mode: service:vpn
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ./web:/usr/share/nginx/html
environment:
- VIRTUAL_HOST=yourdomain.com
database:
image: postgres:latest
depends_on:
- vpn
network_mode: service:vpn
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: exampleuser
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: examplepass
POSTGRES_DB: exampledb
volumes:
- db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
vpn_net:
volumes:
db-data:
In this example:
- The
vpnservice sets up the VPN using the OpenVPN image. - The
webanddatabaseservices are configured to use the VPN container’s network by settingnetwork_modetoservice:vpn. - This configuration ensures that all traffic from the
webanddatabaseservices is routed through the VPN, providing an added layer of security.
By following these steps and examples, you can successfully configure your Docker services to operate securely behind a VPN, enhancing both privacy and security for your applications.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Testing the Setup
Verifying the VPN Connection:
To ensure that the VPN connection is functioning correctly, you can perform a few checks:
- Check the VPN Container Logs:
Inspect the logs of the VPN container to confirm it has started correctly and is connected.
docker logs <vpn-container-name>
- Test the VPN Connection:
Use curl or wget from within a containe using the VPN to check the external IP address. The external IP address should be different than your local IP, and it should match the VPN server’s IP.
docker exec -it <container-name> curl ifconfig.me
Ensuring Services are Behind the VPN:
To verify that the Dockers services you created route all their web traffic through the VPN, you can access the services and check their outgoing IP addresses.
- Check Service IP:
From within the service container, use the following command:
docker exec -it <service-container-name> curl ifconfig.me
The output should match the VPN IP, indicating that the service routes traffic through the VPN.
Common Issues and Solutions
Network Connectivity Issues:
- Issue: Services cannot connect to the internet.
- Solution: Doublecheck the VPN container configuration. Make sure that the network mode is correctly set in the
docker.compose.ymlfile.
- Solution: Doublecheck the VPN container configuration. Make sure that the network mode is correctly set in the
VPN Container Fails to Start:
- Issue: The VPN container doesn’t start / keeps restarting.
- Solution: Check the logs for any errors, and check that the configuration files and credentials you provided are correct. Make sure that the required ports are not bloced by a firewall.
Services Not Routing Through the VPN:
- Issue: Services bypass the VPN and use the host network.
- Solution: Verify the
network_mode: service:vpnsetting in thedocker-compose.ymlfile. Verify that the dependent services start after the VPN container.
- Solution: Verify the
Tips for Troubleshooting
Useful Commands and Logs to Check:
- View Container Logs:
Check the logs for both the VPN container, as well as the created services for any error messages.
docker logs <container-name>
- Inspect Network Settings:
Verify that the network settings of your containers are properly configured.
docker network inspect <network-name>
- Check IP Routes:
Verify the IP routing tables within the containers to ensure that traffic is being routed through the VPN.
docker exec -it <container-name> ip route
Community and Support Resources:
Docker Documentation: The official Docker documentation is the defacto resource for troubleshooting and best practices when using Docker.
OpenVPN Documentation: The OpenVPN documentation will help you in determining specific configurations and in general troubleshooting.
Community Forums: Search your issue on community forums such as Stack Overflow , Docker Community Forums , and Reddit .
Conclusion
In this guide, we covered the essential steps to set up a Docker Compose file with VPN integration. We discussed selecting a suitable VPN provider, setting up a VPN container in Docker, and modifying a Docker Compose file to route service traffic through the VPN. We also explored methods to test and verify VPN-secured Docker services.
Using a VPN with your Docker services significantly enhances security and privacy by ensuring secure communication between distributed services and protecting sensitive data.